When you're talking about the backbone of modern communication, you're really talking about Corning fiber optic cable. They’re not just a player in the industry; they literally invented the first low-loss optical fiber, setting the standard for the performance and reliability we rely on today. Their materials are the bedrock that carriers, data centers, and wireless providers use to build the networks of the future.
The Bedrock of High-Speed Networks
Network operators are constantly juggling three major pressures: an unending hunger for more bandwidth, the need for rock-solid reliability, and the demand to build networks that can scale for tomorrow. The strain on performance is immense, from streaming 4K video to powering AI-driven data centers.
Corning engineers their fiber optic cable to solve these exact problems. It provides a tough, dependable pathway for data, because the truth is, the quality of your physical layer determines the performance of your entire network. A system built with cheap, inferior materials will always be plagued by signal loss, constant maintenance headaches, and an inability to grow. On the other hand, building on a foundation of premium Corning fiber is an investment in longevity and adaptability.
Meeting Today's Core Infrastructure Challenges
Corning's place in telecommunications isn't just as a supplier—they're pioneers. They completely changed global communications back in 1970 by inventing the first low-loss optical fiber and later hit the incredible milestone of delivering their one billionth kilometer of it.
Today, their leadership is clear. As the worldwide market leader, Corning and a few other key manufacturers hold over 40% of the global market share. This shows just how vital their products are to hundreds of thousands of networks.
For anyone building a network, this leadership brings real-world advantages:
- Meeting Bandwidth Demand: Corning fiber offers practically limitless bandwidth, which is critical for handling 5G, cloud computing, and massive IoT deployments.
- Ensuring Unwavering Reliability: Their precision manufacturing process means less signal degradation and fewer physical weak points, resulting in less downtime and lower operating costs.
- Enabling Future Scalability: When you install high-quality fiber now, you can easily upgrade the network electronics later without having to rip and replace the core cabling.
The recipe for a high-performance network that lasts is simple: combine best-in-class materials from Corning with the expert engineering and installation of a trusted partner.
Of course, a successful deployment goes deeper than just the cable itself. It requires a solid understanding of the physical groundwork, including things like foundation excavation for utilities. From the trench to the final termination, every single layer of the system has to be built for durability and peak performance.
A Practical Guide to Corning’s Fiber Optic Cable Families
Choosing the right Corning fiber optic cable isn't about memorizing part numbers; it's about understanding the job that needs to get done. Think of it like a contractor picking the right tool—you wouldn't use a finish nailer to frame a house. Each Corning cable family is engineered for a specific environment, and matching the cable to the real-world conditions is the first step toward a reliable, long-lasting network.
We’re talking about the difference between a cable that can survive being buried in frozen ground for 30 years and one designed to snake through the cramped, high-density pathways of a modern data center. Let’s break down the main players.
Built for the Outdoors: Rugged and Resilient
When you run fiber outside, you're exposing it to a whole world of threats: moisture, extreme temperature swings, physical stress, and even curious critters. The cable’s job is to act as a shield, protecting the delicate glass strands inside.
Corning's ALTOS® family is the workhorse for these tough, outdoor plant (OSP) applications. The magic is in its loose-tube design. Instead of being held rigidly, the fibers float inside protective buffer tubes, which are then bundled inside a heavy-duty outer jacket. This construction gives the fibers breathing room to handle the expansion and contraction from brutal temperature cycles, ensuring your signal stays stable through freezing winters and blazing summers. It’s perfect for aerial runs or pulling through conduit.
For direct-burial applications where the cable faces constant ground pressure and the threat of rodents, you’ll want an armored version. It’s the same proven design, just with an extra layer of metallic protection to keep the core safe.
The infographic below shows just how critical this foundational fiber layer is to meeting the core requirements of any modern digital infrastructure: performance, reliability, and the ability to scale.
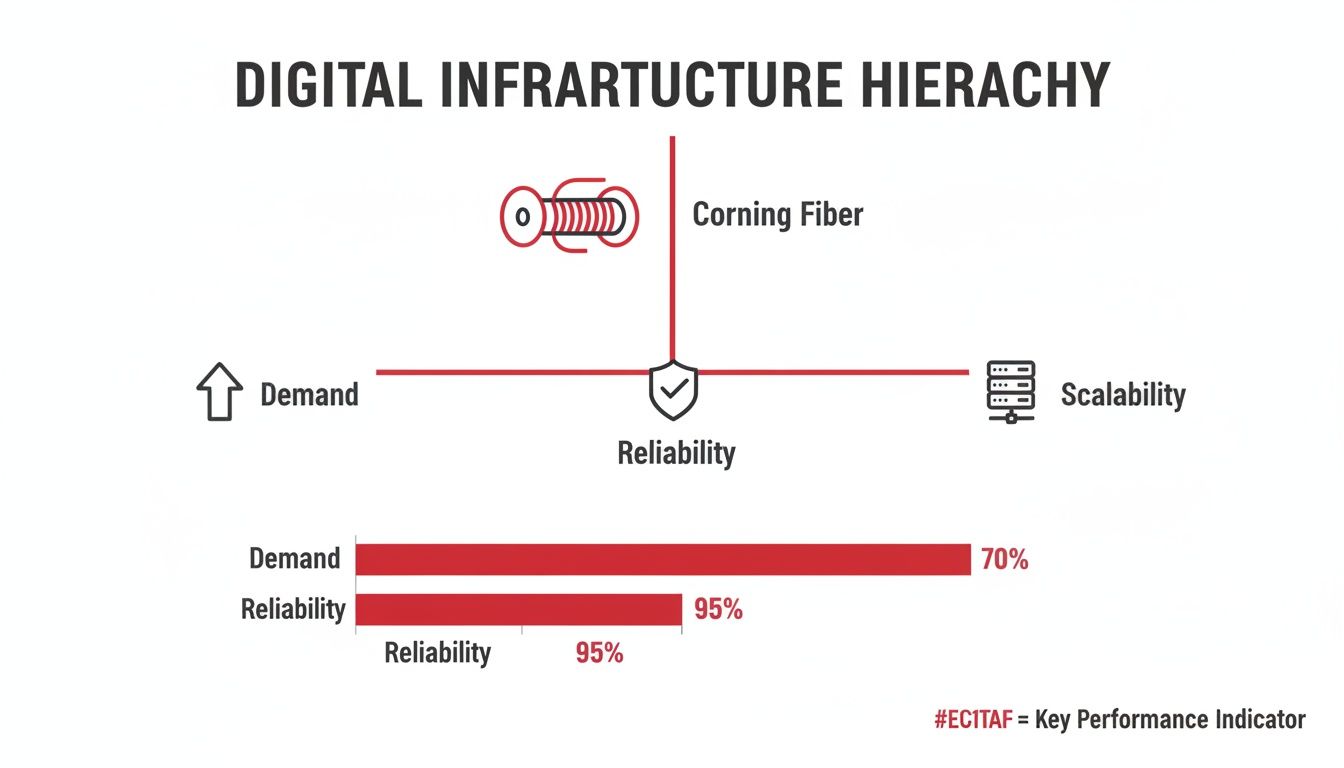
As you can see, a solid fiber backbone isn't just a component; it's what makes achieving those high-level performance metrics possible.
Built for Density: High-Count Indoor Solutions
Inside a building, especially a data center, the challenges are entirely different. The enemy isn't the weather; it's the lack of space. The goal is to pack as much connectivity as possible into the smallest footprint without creating a tangled mess. This is where high-density designs like ribbon and MiniXtend® cables come into play.
If a loose-tube cable is like an armored convoy, a ribbon cable is more like a perfectly organized multi-lane highway. Instead of individual fibers, it arranges up to 24 fibers into a flat, tape-like strip. These ribbons are then stacked, allowing for massive fiber counts in a surprisingly small cable.
This architecture delivers two huge wins for data center and enterprise environments:
- Incredible Space Savings: Ribbon cables take up far less room in crowded trays and conduits, which improves airflow and makes everything easier to manage.
- Faster Splicing: A technician can use a mass-fusion splicer to connect an entire 12-fiber ribbon in a single shot. This absolutely demolishes the time and labor costs compared to splicing one fiber at a time.
For network planners, the choice between loose-tube and ribbon cable is a classic strategic trade-off: environmental toughness for the outdoors versus maximum density and installation speed for the indoors.
Corning's MiniXtend® cables take this density-first approach even further. By using innovative binder technology and even smaller buffer tubes, they cram more fibers into an even tinier overall diameter. They are an absolute lifesaver when you're trying to pull more capacity through already-congested conduits. A great example is the Corning 432 Strand Single-Mode OS2 Plenum Fiber Optic Cable, which shows how this high-density engineering is packaged for demanding indoor backbone applications.
Corning Fiber Optic Cable Families At-a-Glance
To help visualize these differences, here's a quick breakdown of some of the most common Corning cable families and where they fit best. This is a great starting point for matching a product line to your project's specific needs.
| Cable Family | Primary Environment | Key Feature | Best Use Case Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALTOS® | Outdoor (Aerial, Duct, Buried) | Loose-tube design for environmental protection | A long-haul telecom link running between two cities. |
| RocketRibbon® | Outdoor / Indoor | High-density ribbon with easy-to-access subunits | A campus backbone connecting multiple buildings. |
| MiniXtend® | Indoor (Data Center, Ducts) | Extremely high density, small cable diameter | Upgrading connectivity in crowded data center conduits. |
| Freedm® | Indoor / Outdoor | All-dielectric, flame-retardant jacket | A versatile cable for running from outside into a building riser. |
Ultimately, understanding these purpose-built designs allows network planners and engineers to select the exact right solution, ensuring the physical infrastructure is just as robust and forward-thinking as the services running over it.
Choosing Between Single-Mode and Multi-Mode Fiber
When you're laying out a new network, one of the first calls you have to make is whether to go with single-mode or multi-mode fiber. This isn't just a minor technical detail—it's a foundational decision that will define your network's reach, data capacity, and budget for years to come. Getting this right from the start by selecting the best fiber optic cable Corning offers ensures your infrastructure is ready for whatever comes next.
Let's break it down with a simple analogy. Think of single-mode fiber as a laser pointer. It shoots a single, tightly focused beam of light down an incredibly narrow path—its core is only 9 microns wide. Because the light travels with almost no distortion, it can go for miles and miles. This makes it the undisputed king for long-haul telecom, ISP backbones, and even transoceanic cables.
Multi-mode fiber, on the other hand, is more like a flashlight. It has a much wider core (50 or 62.5 microns) that allows multiple beams of light (or modes) to bounce their way down the fiber all at once. This approach is fantastic for moving a ton of data over shorter distances, like wiring up an office building, connecting buildings on a corporate campus, or linking racks inside a data center.
Single-Mode Fiber: The Long-Distance Champion
When you need distance and massive bandwidth potential, single-mode fiber is the only real choice. The industry standard, OS2, is what you'll find in most Corning long-haul products. Since that single beam of light travels in a nearly perfectly straight line, signal loss over distance is astonishingly low. This means you can run networks for tens, or even hundreds, of kilometers before needing a signal booster.
This is the lifeblood for:
- Telecommunication Carriers: Connecting cities, states, and countries with the high-speed links that form the internet's backbone.
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs): Building out the core infrastructure that brings broadband to our homes and businesses.
- Large Campus Networks: Tying together buildings spread across a university, hospital, or corporate park.
Now, the light source for single-mode is a high-powered laser, which costs more than the LEDs or VCSELs used for multi-mode. But here's the catch: for long-haul projects, the total system cost is often lower because you save a fortune by not having to install and power signal repeaters every few kilometers. It's a classic case of smart upfront investment paying off.
Multi-Mode Fiber: The Data Center Powerhouse
When your cable runs are measured in feet and meters instead of miles, multi-mode fiber really comes into its own. The wider core you find in OM3, OM4, and the newer OM5 standards is designed to work with much cheaper light sources, like Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers (VCSELs). This makes the transceivers—the little pluggable modules at each end of the cable—significantly more affordable.
For anyone running a data center, the cost difference on hundreds or even thousands of short-reach server and switch connections is huge. Multi-mode delivers the high-bandwidth muscle you need for rack-to-rack traffic without the premium price tag of long-distance optics.
This cost-effectiveness has made multi-mode the standard for high-density environments. It’s perfect for connecting servers to top-of-rack switches, linking network gear within a data hall, or wiring the backbone in a corporate high-rise. If you're planning an indoor installation, you can explore plenum-rated fiber optic cables specifically designed for safe use in these spaces.
Making the Right Financial and Technical Decision
Ultimately, the choice comes down to a trade-off that directly impacts your budget and future upgrade plans. Multi-mode optics are cheaper, but the fiber cable itself is often a bit more expensive per foot. Conversely, single-mode cable is cheaper, but the transceivers cost more. The decision really hinges on your required distance and the sheer number of connections you need to light up.
This distinction is more critical than ever. The global fiber optic cable market, valued at USD 13 billion in 2024, is expected to explode to USD 34.5 billion by 2034. This incredible growth is being fueled by the rollout of 5G and the non-stop expansion of data centers—two areas where both single-mode and multi-mode play essential roles. You can find the full market research on this at gminsights.com.
By understanding where each fiber type excels, you can design and build a network that's not just cost-effective and technically sound today, but also ready to scale for the demands of tomorrow.
Selecting the Right Cable Construction and Armor
Once you've figured out the type of glass you need, the next big decision is the cable's physical construction. This is where you move from the "what" to the "how"—how the cable will survive in the real world. The right fiber optic cable corning is more than just a conduit for light; it's a ruggedized shield built to handle the environment it's placed in. This choice has a huge impact on your installation time, operational costs, and the overall lifespan of your network.
Think of the cable's structure as its survival gear, hand-picked for the journey ahead. A cable being pulled through a clean, protected indoor conduit needs a very different set of defenses than one being buried directly in rocky soil. Two of the most critical decisions here are the fiber arrangement—loose-tube versus ribbon—and the type of protective armor you wrap it in.
The Strategic Advantage of Ribbon Cable
For massive projects like Fiber-to-the-x (FTTx) deployments or data center build-outs, speed is everything. This is exactly where ribbon cable gives you a massive strategic advantage. Instead of dealing with hundreds of individual fibers, a ribbon cable arranges up to 24 fibers into a neat, flat strip. These ribbons are then stacked inside the cable, allowing for incredibly high fiber counts in a surprisingly compact design.
But the real magic happens during splicing. Using a specialized tool called a mass-fusion splicer, a technician can fuse an entire 12-fiber ribbon in a single shot. Compare that to the painstaking process of splicing one fiber at a time, and the time savings are enormous. On a high-count backbone cable, this efficiency can easily shave days—or even weeks—off a project timeline.
In environments where density and rapid deployment are paramount, choosing ribbon cable is an investment in efficiency. It streamlines the most time-consuming part of the installation, ensuring the network is lit up faster and with lower labor expenses.
The compact design also helps you make the most of limited space. In crowded data center trays or congested underground ducts, a smaller cable diameter lets you pack in more capacity, which also improves airflow and makes future maintenance a whole lot easier.
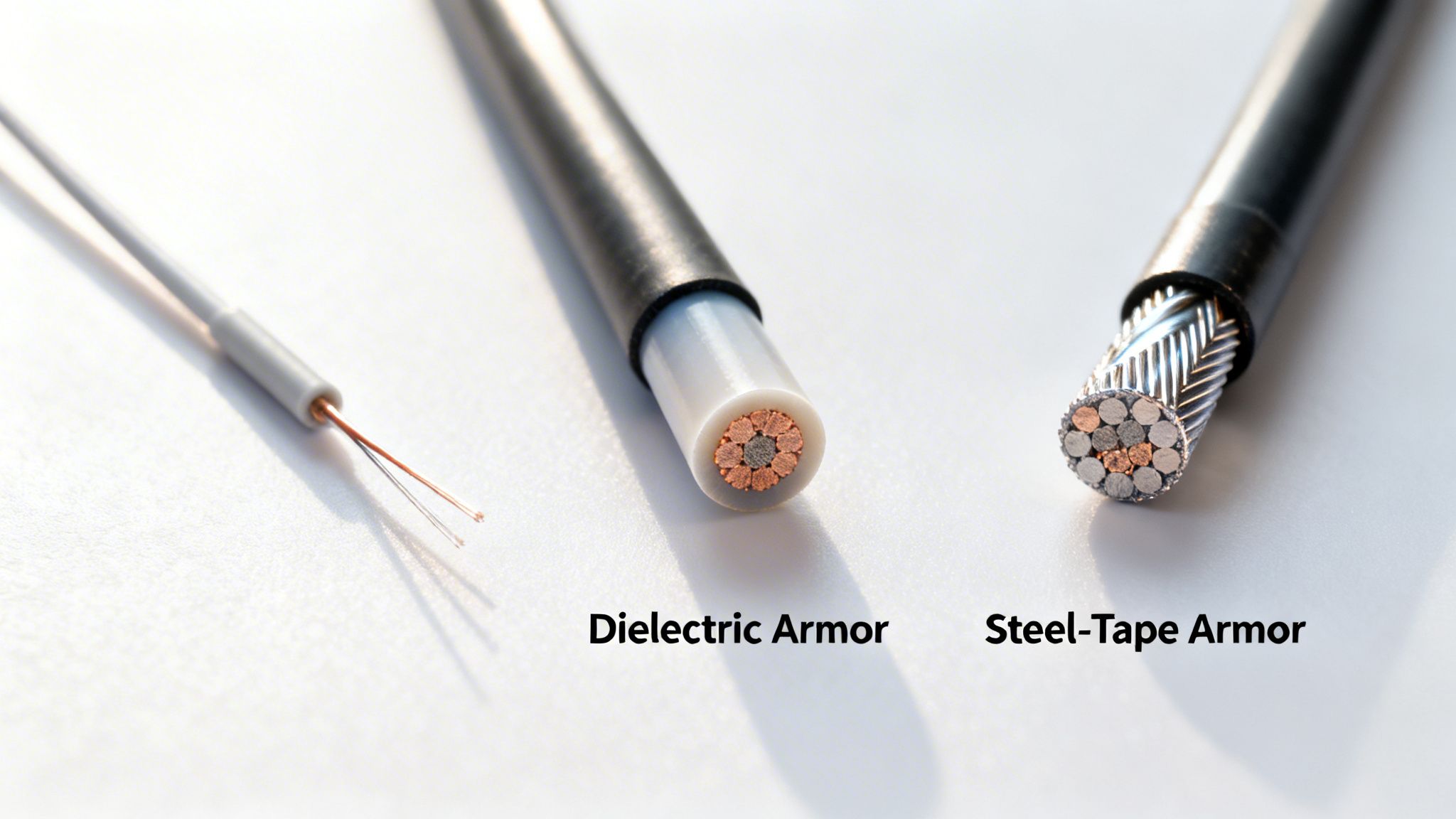
Armoring Your Investment: Dielectric vs. Steel
After you’ve settled on the fiber construction, the next critical question is how you’re going to protect it. Cable armor is the first line of defense against physical threats, and the two main options—dielectric and steel-tape—are built for very different battlefields.
Picking the right one is crucial for preventing expensive repairs and frustrating network downtime. Each armor type is engineered to counter a specific set of environmental hazards.
Dielectric Armor: This armor is completely non-metallic. It typically uses incredibly strong aramid yarns (the same material in bulletproof vests) and fiberglass rods for strength. Its main benefit? It doesn’t conduct electricity. This makes it the only choice for any cable installed near high-voltage power lines, whether you're lashing it to a utility pole or sharing an underground conduit. Dielectric armor prevents electromagnetic interference (EMI) and eliminates the terrifying risk of an electrical fault traveling down your cable and frying your sensitive network equipment.
Steel-Tape Armor: When you’re burying a cable directly in the ground, its biggest enemies are crushing forces from soil and rocks, and the sharp teeth of rodents like gophers. Steel-tape armor is a formidable defense against both. A corrugated steel layer wrapped around the cable core gives it excellent crush resistance and makes it nearly impossible for critters to chew through to the delicate glass inside. It’s the go-to solution for direct-burial jobs, giving you peace of mind that your cable can withstand life underground. And if you’re looking at the full picture, it's also worth learning how to choose the right faceplates for different fiber installations, another key component of a professional build-out.
At the end of the day, selecting the right construction and armor is all about foresight. When you carefully match the fiber optic cable corning product to its specific deployment environment, you’re building a network that isn't just high-performing, but tough enough to do its job reliably for decades to come.
Mastering Installation, Splicing, and Testing
Choosing the right cable is just the starting point. The real magic happens in the field, where a spool of high-tech fiber is transformed into the backbone of a high-performance network. Honestly, the difference between a rock-solid system and one that gives you constant headaches often boils down to the skill and precision of the installation team. It’s a discipline where every detail matters.
For instance, every cable has a minimum bend radius. Think of it as the tightest corner you can take without damaging the delicate glass fibers inside. Go beyond that limit, even for a moment, and you risk creating tiny fractures that kill signal quality or lead to total failure. The same goes for pulling tension. Yanking too hard on a cable during installation can stretch it, permanently damaging the fiber. Following these physical rules isn't optional—it's fundamental to a successful build.
The Art and Science of Precision Splicing
Connecting two fiber optic cables isn’t like twisting a couple of copper wires together. The goal is to create a perfectly seamless, permanent bond with virtually zero signal loss. The industry gold standard for this is fusion splicing, a process that creates a connection just as strong and clear as the original, uninterrupted fiber.
A fusion splicer is an incredible piece of equipment that handles a few critical steps with microscopic precision:
- Stripping and Cleaning: First, our technicians carefully strip back the protective coatings from each fiber end. Then, they clean them with isopropyl alcohol until they are completely free of any dust or residue.
- Cleaving: Next, each fiber is precisely cut—or "cleaved"—to create a perfectly flat, mirror-smooth surface at an exact 90-degree angle.
- Alignment and Fusion: The splicer then uses tiny motors and high-powered cameras to align the two fiber cores with sub-micron accuracy. Once they’re lined up perfectly, it creates a small electric arc that melts the glass ends, fusing them into a single, continuous piece.

When done right, a fusion splice creates a connection with an optical loss of less than 0.02 decibels (dB). That's a signal loss so small it’s almost impossible to measure. For projects with high-count ribbon cables, mass-fusion splicers can even perform this delicate operation on all 12 fibers at once, which massively speeds up deployment time.
The Final Verdict: Post-Installation Testing
Once the last splice is complete, we’re still not done. The final, non-negotiable step is to put the entire network through a rigorous testing process. This gives our clients definitive proof that the job was done right and, just as importantly, establishes a performance baseline for any future maintenance or troubleshooting.
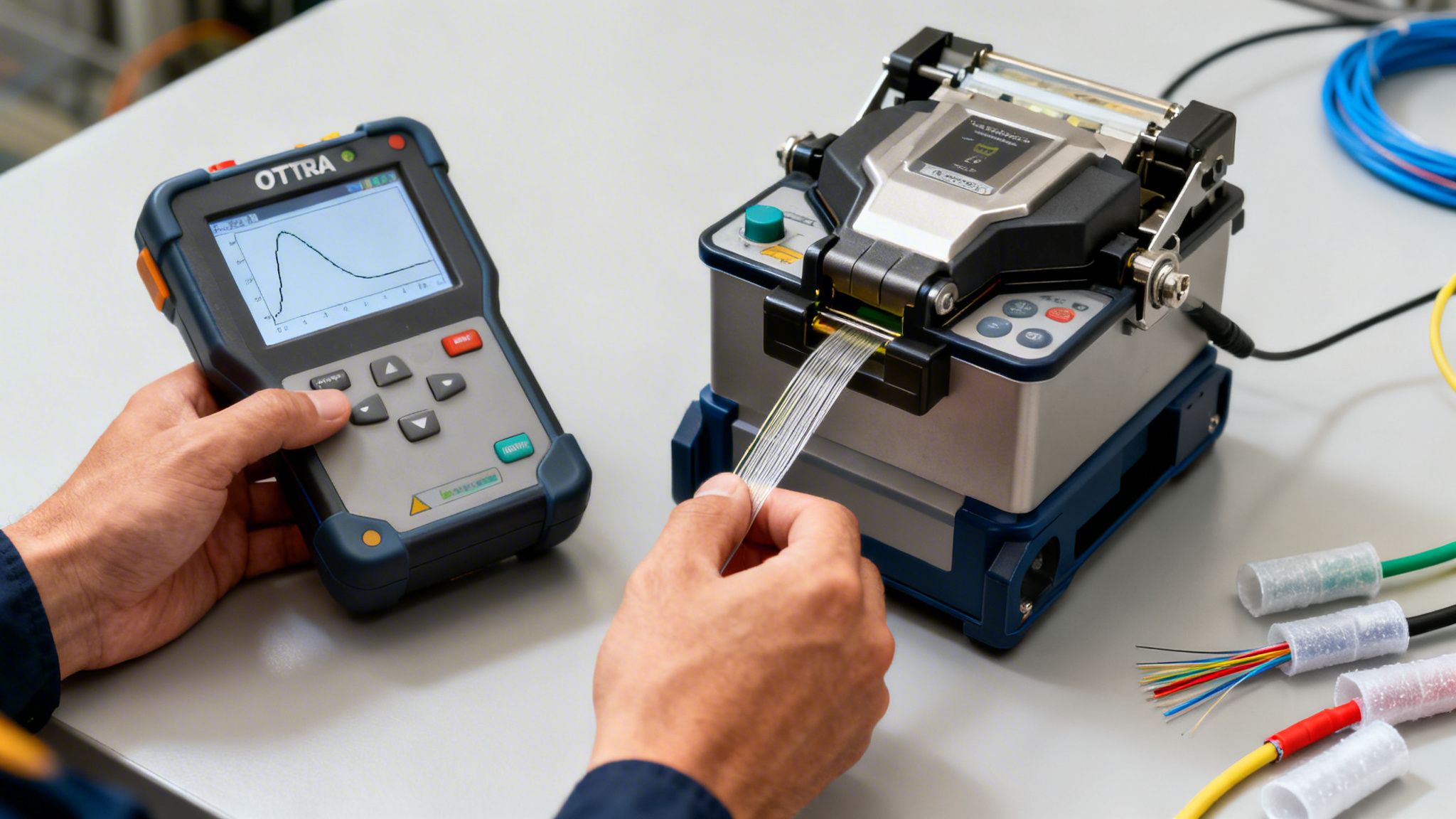
Our go-to tool for this is the Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR). It works by sending a tiny pulse of light down the fiber and then meticulously measuring every reflection that scatters back. By analyzing these signals, our technicians can get a complete picture of the entire cable run from start to finish.
An OTDR trace is like a detailed X-ray of your fiber network. It precisely locates splices, connectors, and any potential issues like sharp bends or fiber breaks, measuring the signal loss at every single point along the path.
This data is invaluable. It certifies that the installation meets—and often exceeds—industry standards and acts as a detailed "birth certificate" for the network. If a performance issue pops up years down the road, we can simply run a new OTDR test and compare it to the original baseline. This allows us to find the exact location and nature of the problem in minutes, not days.
This level of meticulous work is more critical now than ever. The explosion in AI is fueling massive growth in Corning's Optical Communications segment, with data center product shipments nearly doubling in a single quarter. Big deals, like a $6 billion commitment from Meta, mean Corning is running at full capacity, and demand is often outstripping supply. You can explore more about this trend and what it means for the industry. In this environment, you need a partner like Southern Tier Resources who can deliver flawless turnkey solutions, ensuring every installation is built right and ready to scale from day one.
Putting It All Together: From Cable to End-to-End Network Success
Choosing a world-class fiber optic cable from Corning is a fantastic start, but it's just that—a start. Even the best materials don't guarantee a high-performance network on their own. The real magic happens when that premium cable is expertly engineered, installed, and brought to life.
Think of it like building a high-performance engine. You can have the best pistons and camshafts, but they're just a pile of expensive parts until a master mechanic assembles and tunes them perfectly. A fiber network is an ecosystem, and every single component, from the cable to the final splice, needs to be executed with absolute precision.
From Blueprint to a Living Network
This is where a true turnkey partner comes in. They manage the entire project lifecycle, ensuring the initial design concept translates flawlessly into a reliable, operational network. It’s a detailed journey from blueprint to activation, and having one team oversee it all prevents critical details from falling through the cracks.
A successful network build isn't a single event; it's a multi-stage process demanding specialized skills at every turn.
- Meticulous Design and Permitting: This is the foundation. It involves creating detailed route plans while navigating the complex web of local regulations and right-of-way permissions.
- Expert Splicing and Termination: Here, skilled technicians execute flawless fusion splices and connections. This is where signal integrity is preserved and optical loss is minimized.
- Rigorous Testing and Documentation: Every strand of fiber is certified using OTDRs. We provide clients with detailed as-built plans, creating a vital roadmap for future maintenance and upgrades.
- Dedicated 24/7 Maintenance: The job isn't done when the lights turn on. We offer ongoing support to keep the network at peak performance and rapidly address any service interruptions.
A genuine partnership doesn't end at go-live. It extends through the entire operational life of the infrastructure, giving you the peace of mind that your investment will continue delivering value for years to come.
The demand for this kind of expertise is exploding. The fiber optics market is projected to more than double, growing from USD 3.2 billion in 2024 to USD 6.8 billion by 2029. This surge is fueled by the massive data appetites of AI, cloud computing, and the IoT.
As this race to build better, faster infrastructure accelerates, having a partner who can deliver a complete solution—backed by 24/7 maintenance and precise documentation—is no longer a luxury. It's essential. You can read the full analysis on the growing fiber optics market to dive deeper into these trends. This partnership model ensures the network we build not only meets today’s highest standards but is ready for whatever comes next.
Your Questions, Answered
Diving into fiber optics, especially for a major infrastructure project, naturally brings up a lot of questions. We get it. Here are some of the most common things we discuss with clients when planning a network build with Corning fiber optic cable.
We’ve put together clear, straightforward answers to help you understand the critical factors that make the difference between a good network and a great one.
What Really Sets Corning Fiber Apart?
It all comes down to a legacy of innovation, incredibly tight manufacturing, and a serious commitment to quality control. Corning didn't just join the fiber optic industry; they essentially created it by inventing the first low-loss optical fiber. That deep-rooted expertise in material science is why their fiber consistently delivers better performance—we're talking lower signal loss (attenuation) and the kind of physical toughness that stands up to real-world conditions over decades.
For network builders and technicians in the field, this consistency is huge. It means fewer surprises during installation, performance that lines up perfectly with the pre-build models, and ultimately, a rock-solid network for the end-user.
How Does the Right Cable Choice Lower Future Maintenance Bills?
Picking the right cable from day one is one of the smartest ways to control your long-term operational costs. Think about it: opting for a tough, armored cable for a direct-buried run might cost a little more upfront, but it prevents hugely expensive damage from ground shifts or rodents. That single choice helps you sidestep emergency repair calls and crippling network downtime.
A smart upfront investment in the right cable construction and armor is one of the most effective ways to lower the total cost of ownership over the network's entire life.
The same logic applies in a data center. Using high-density ribbon cables makes future upgrades and reconfigurations so much simpler, which translates directly into fewer labor hours for any moves, adds, or changes. The initial investment truly pays for itself in operational savings down the road.
Can You Splice Different Types or Brands of Fiber Together?
The short answer is yes, but it’s a job that demands serious expertise and the right gear. Splicing single-mode to multi-mode fiber, for example, is something you should never do. It creates a massive signal mismatch that will cripple your network's performance right at the connection point.
Even when you're splicing similar fiber types from different manufacturers (like two G.652.D single-mode fibers), you have to be sure their core and cladding dimensions are a perfect match. Our technicians use high-precision fusion splicers and verify every splice with OTDR testing. This ensures the connection has the absolute minimum signal loss and meets the strict industry standards that keep a network running flawlessly.
At Southern Tier Resources, we don't just sell cable; we build high-performance, turnkey networks using world-class Corning fiber. Contact us today to discuss your next infrastructure project.



