When you hear the term fiber network services, you might just picture crews laying cable. But that's only a small part of a much bigger, more complex process. These services cover the entire lifecycle of a fiber optic network—from the initial idea scribbled on a blueprint all the way to maintaining that network for decades to come.
It’s the whole ecosystem of specialized skills needed to design, build, and manage the physical infrastructure that powers our high-speed world.
Understanding Modern Fiber Network Services
Think of a fiber optic cable as a data superhighway. Instead of asphalt, it's made of pure glass, and instead of cars, it carries pulses of light at incredible speeds. Fiber network services are the architects, engineers, and road crews of these digital highways. They don't just lay the pavement; they meticulously plan the routes, manage the traffic flow, and keep everything running smoothly.
This infrastructure is the bedrock of modern life. It's what connects 5G towers, powers massive data centers, and delivers lightning-fast internet to our homes and businesses.

More Than Just Cable
It’s easy to get lost in the physical work, but treating fiber deployment as just a construction project misses the point entirely. These services are a strategic investment in connectivity. The incredible demand for cloud computing, streaming, and advanced wireless technologies simply wouldn't be possible without a solid fiber foundation.
The market reflects this reality. Projections show the global broadband internet services market is set to hit around USD 504.3 billion by 2029, with fiber optic expansion and 5G rollouts being the primary drivers.
At its heart, the job of a fiber network services provider is to turn a vision for digital connectivity into a tangible, high-performance physical asset that works perfectly from day one and for years to follow.
The Ecosystem of Expertise
Bringing a fiber network to life is a team sport, requiring a symphony of different skills. Every single step, from planning the route to the final performance test, builds on the one before it. A mistake in the early design phase can cause major headaches during construction or long-term performance issues.
To give you a clearer picture, let's break down the core services and their roles in a typical project.
Key Fiber Network Services and Their Roles
| Service Category | Core Function | Impact on Network |
|---|---|---|
| Design & Engineering | Creating the strategic blueprint, mapping routes, and securing permits. | Sets the foundation for cost-effectiveness, scalability, and future-proofing. |
| Make-Ready & Construction | Physically preparing the path and installing the conduit and cable. | Determines the physical durability and protection of the network infrastructure. |
| Splicing & Termination | Precisely joining glass fibers and connecting them to network equipment. | Directly affects signal strength, data integrity, and overall network speed. |
| Testing & Documentation | Verifying signal quality, certifying performance, and creating "as-built" records. | Ensures the network meets industry standards and simplifies future maintenance. |
| Maintenance & Support | Providing ongoing monitoring, emergency repairs, and proactive upkeep. | Guarantees long-term reliability, minimizes downtime, and protects the investment. |
Each of these stages is critical. For instance, understanding the technical nuances of something as specific as a fiber optic ST connector can make all the difference during the termination phase.
These individual disciplines come together to form the backbone of all modern broadband and telecom services. Getting each one right is non-negotiable for building a network that can meet today's demands and scale for tomorrow's.
Mapping the Fiber Deployment Lifecycle
Building a fiber network isn't a single event; it's a journey. Think of it like building a custom home. You don't just show up with a hammer and start framing walls. You begin with a detailed architectural plan and follow a sequence of specialized construction phases, one after the other. The fiber deployment lifecycle is the same kind of end-to-end process, where each stage builds on the last to create a network that’s robust, reliable, and ready for decades of service.
This journey is all about turning a strategic vision into a high-performance physical asset. When you understand the full lifecycle, you see why a coordinated, expert approach is the only way to deliver a complex network on time and on budget. It’s a process with distinct, yet deeply connected, phases.
Phase 1: Network Design and Engineering
This is the architectural stage. Here, the digital blueprint for the entire network gets hammered out. Engineers figure out the most efficient and cost-effective routes for the fiber cables, taking into account everything from rough terrain and existing infrastructure to what the network will need to handle years down the road. It’s a lot more than just drawing lines on a map.
Key activities during this stage include:
- Feasibility Studies: A hard look at the project's viability, potential return on investment, and the big-picture requirements.
- Route Planning: Using advanced software to map out the exact paths for the fiber, whether it’s strung on poles, buried underground, or a mix of both.
- Capacity Planning: Doing the math to determine how many fiber strands are needed to meet today's demand while leaving room for future growth.
This foundational work sets the tone for everything else. A poorly designed network can easily lead to cost overruns of 15-20% or more from hitting unexpected construction snags and inefficient routing.
Phase 2: Make-Ready and Permitting
With the blueprint in hand, the next job is to get the physical path ready for construction. This phase, often called make-ready engineering, is the critical groundwork of securing all the necessary permissions and making sure the chosen route is clear and accessible. It’s the equivalent of getting building permits and clearing the land before you can even think about pouring a foundation.
This means navigating a complicated web of logistics and red tape. For aerial builds, you’re coordinating with utility companies to get access to their poles, which might mean moving existing cables or even replacing poles to handle the extra load. For underground projects, it involves securing rights-of-way and getting excavation permits from local authorities.
Make-ready and permitting is often the single most time-consuming part of the entire lifecycle. Proactive management and solid relationships with utility owners and local governments are non-negotiable if you want to keep a project from getting bogged down.
Phase 3: Outside Plant (OSP) Construction
This is the part most people picture when they think of fiber deployment—the actual physical installation of the network. Skilled crews take the engineered designs and bring them to life, laying the infrastructure that will house and protect the delicate glass fibers.
Construction methods really depend on the design:
- Underground Construction: This could be trenching, directional boring to tunnel under obstacles like roads, or plowing to install protective conduit. This method gives the fiber the best protection from weather and accidental damage.
- Aerial Construction: Crews string the fiber optic cable between utility poles. This is often a faster and more cost-effective approach in areas where there's already a good pole infrastructure in place.
The quality of OSP construction has a direct and lasting impact on the network’s durability and resilience.
Phase 4: Splicing and Commissioning
Once the physical cable is in place, the most precise and delicate work begins. Fiber splicing is the art of joining two individual glass strands together with microscopic precision. A single misalignment—smaller than the width of a human hair—can cripple the signal. Highly trained technicians use fusion splicers to literally melt the glass ends together, creating a perfect, seamless connection.
After splicing comes the final exam: testing and commissioning. Technicians send light signals through the fibers and use specialized equipment like Optical Time Domain Reflectometers (OTDRs) to check the signal strength, hunt for any flaws, and make sure every connection is up to snuff. This final quality check is what confirms the network is ready to "go live" and deliver flawless service.
For organizations that want a fully integrated approach, partners offering turnkey network solutions can manage this entire lifecycle from a single point of contact, smoothing out the whole process.
Specialized Fiber Services for Critical Demands
Beyond the everyday network builds, there’s a whole other class of fiber network services dedicated to powering the most critical digital infrastructure on the planet. We're talking about the high-performance nervous systems for data centers, wireless networks, and massive enterprises—places where flawless, high-capacity connectivity isn't just a goal, it's a requirement.
In these environments, there is absolutely zero tolerance for latency or downtime. This demands a level of precision and expertise that goes far beyond a typical fiber-to-the-home deployment. These complex projects move through a well-defined lifecycle, starting with meticulous design and engineering, shifting to physical construction, and culminating in rigorous, comprehensive testing.
This process is how a conceptual blueprint becomes a fully commissioned, high-performance network asset, ready to carry mission-critical traffic.
Powering the Cloud with Data Center Fit-Outs
Data centers are the engines of our digital economy, and the connectivity inside them is just as important as the connections coming to them. A data center fit-out is a highly specialized service that involves installing all the structured cabling and fiber infrastructure within these massive facilities. The entire goal is to create a high-density, ultra-low-latency environment that can handle unbelievable amounts of traffic between thousands of servers.
This isn't like standard outside plant construction. The work takes place in a controlled but incredibly complex space. Technicians have to navigate intricate cable pathways, work around cooling and power systems, and terminate thousands of connections with absolute precision. A single poorly seated connector can create a bottleneck that degrades the performance of countless applications.
Wireless Backhaul: The Unseen Backbone of 5G
The incredible speeds 5G promises are completely dependent on a hidden fiber optic backbone. Wireless backhaul is the fiber network that connects individual cell towers—from the small cells on streetlights to the massive macro towers—back to the core network.
Think of each cell tower as a local on-ramp to the internet superhighway. The fiber is the highway itself. Without a high-capacity fiber link, a 5G tower would be like an eight-lane on-ramp feeding into a single-lane dirt road. It just can't handle the traffic. This service is absolutely essential for mobile carriers expanding their networks to meet the explosive demand for mobile data, streaming video, and the Internet of Things.
Wireless backhaul is the perfect synergy: you get the flexibility of wireless access at the edge, all powered by the immense, reliable capacity of a fiber core. It's the fundamental infrastructure that makes modern mobile communication possible.
Dark Fiber: Unlocking Ultimate Control and Scalability
Imagine leasing an entire empty highway just for your own traffic. You get to choose the cars, set the speed limits, and manage everything yourself. That's the essence of dark fiber. This service involves leasing unused, unlit fiber optic strands from a network owner. The customer is then responsible for providing the electronics that "light up" the fiber and manage the network.
While this requires more in-house expertise, the benefits are unmatched:
- Virtually unlimited bandwidth: Your capacity is only limited by the equipment you connect at either end.
- Enhanced security: Your data is traveling on a private, physically separate network.
- Ultimate control: You manage the network protocols and equipment, giving you total command over performance.
This is a popular strategy for large enterprises, financial institutions, and cloud providers connecting major data centers. The market is growing fast, recently valued at around USD 8.06 billion and projected to grow at nearly 12.4% annually. Long-haul networks are the most common application, with the telecom sector being the biggest user. You can explore detailed insights on the dark fiber industry for a deeper look at the market dynamics.
These specialized services all depend on expert execution, especially when it comes to the precision work of joining fiber strands together. To get a better handle on this critical step, you might find our guide on how to properly splice fiber optic cable helpful.
Defining Success with KPIs and Testing Standards
How can you be certain a brand-new fiber network is truly built to last? You don’t have to guess. The answer lies in rigorous, data-driven testing and a clear set of performance metrics that prove the quality of the installation.
Without these verifiable standards, a network is just a collection of cables. With them, it becomes a certified, high-performance asset ready for decades of reliable service.
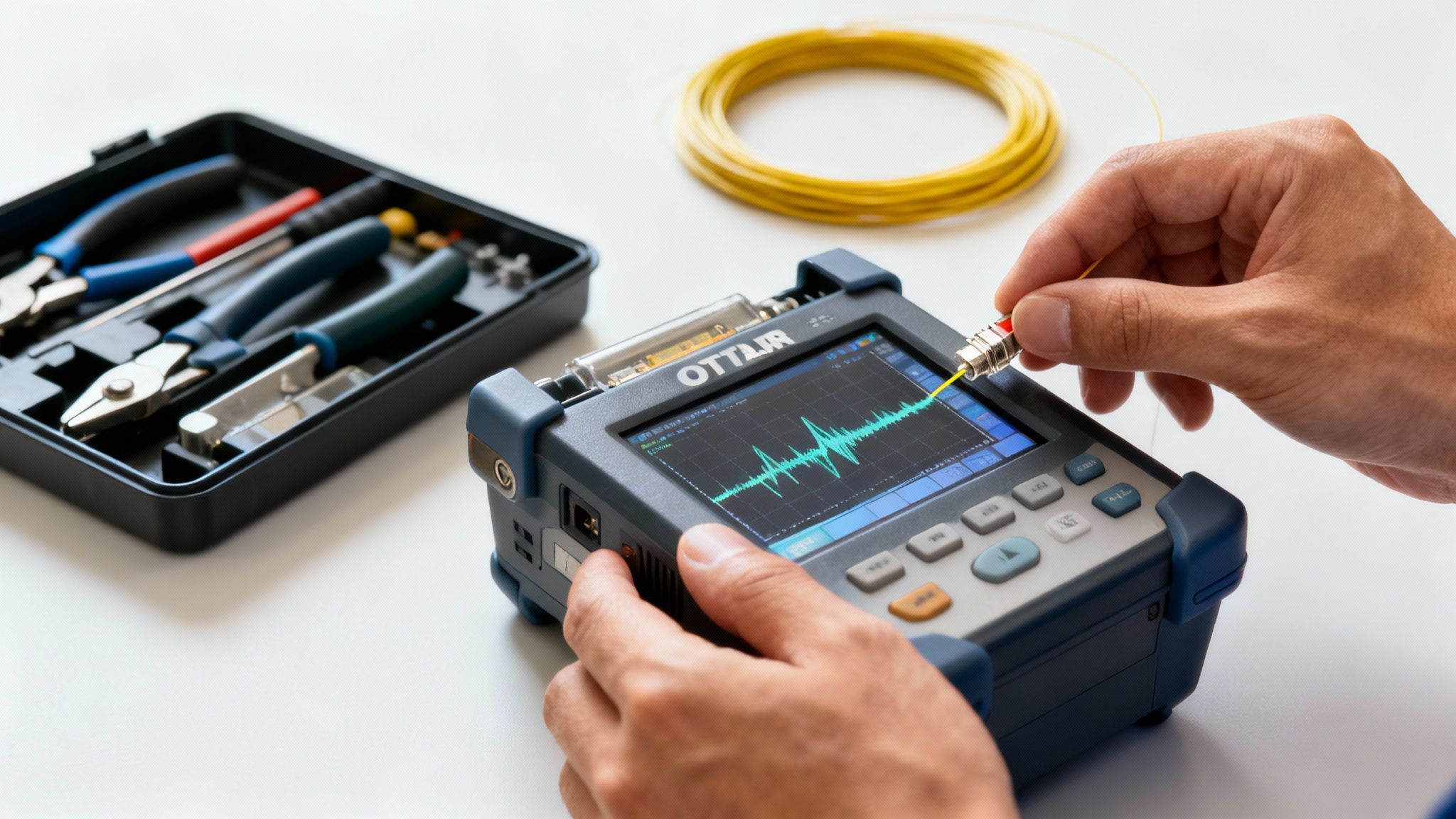

This verification process isn't just a final checkmark. Meticulous quality assurance performed throughout the deployment lifecycle is what prevents future outages, dramatically reduces long-term maintenance costs, and guarantees your network delivers the speed and reliability your users demand from day one.
The Language of Light: Key Performance Indicators
To measure the health of a fiber network, technicians rely on specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Think of these like vital signs for your infrastructure. Just as a doctor checks your blood pressure and heart rate, network experts measure how well light travels through the glass fibers.
Two of the most critical KPIs are:
- Insertion Loss (IL): This measures the total amount of light, or signal strength, lost as it travels from one end of the cable to the other. Every connection, splice, and imperfection contributes to this loss. Lower numbers are better, indicating a strong, clear signal.
- Optical Return Loss (ORL): This measures the amount of light that gets reflected back toward the source. High reflections can corrupt the signal and disrupt network performance. Higher numbers are better here, showing that most of the light is reaching its destination.
These metrics aren't just technical jargon; they directly translate to real-world performance. A network with poor IL and ORL values will suffer from slow speeds, dropped connections, and unreliable service.
A network is only as strong as its weakest link. Rigorous testing with precise KPIs ensures that every single component—from the longest cable run to the smallest connector—meets exacting industry standards for performance and longevity.
Essential Tools for Network Verification
Achieving these standards requires specialized equipment operated by skilled technicians. The most indispensable tool in this process is the Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR). An OTDR acts like a sophisticated radar system for the fiber optic cable.
It works by sending a powerful pulse of light down the fiber and then meticulously analyzing the light that reflects back. By measuring the timing and strength of these reflections, the OTDR can create a detailed "map" of the entire cable run. This allows technicians to:
- Pinpoint the exact location of splices and connectors.
- Measure the specific signal loss at each event.
- Identify faults, such as sharp bends or breaks in the fiber, with pinpoint accuracy.
This capability is essential not only for certifying a new installation but also for rapidly troubleshooting any issues that may arise later. The detailed data it provides is the ultimate proof of a quality installation.
To give you a clearer picture, here’s a breakdown of the most important performance tests that ensure your network is ready for anything.
Essential Fiber Optic Testing Metrics
| Metric (KPI) | What It Measures | Why It's Important |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion Loss (IL) | Total signal power lost along a fiber link. | Low IL ensures a strong, reliable signal reaches its destination, preventing data errors and slow performance. |
| Optical Return Loss (ORL) | Amount of light reflected back to the source. | High ORL means less signal interference and better overall network stability. |
| Attenuation | The gradual weakening of signal strength (in dB/km). | Verifies that the fiber cable itself meets quality standards and has no manufacturing defects or damage. |
| Reflectance | The amount of light reflected at a single point, like a connector. | Pinpoints problematic connections that can corrupt data and cause network instability. |
These metrics, when properly measured and documented, provide a complete health report for your network infrastructure.
This level of quality is particularly vital for modern mobile networks. Today, more than 85% of new 5G base stations globally are connected via fiber, underscoring its role in high-speed wireless backhaul. You can explore more data about the global fiber optics market share to see regional trends. By adhering to these testing standards, fiber network services providers ensure that this critical infrastructure is built to perform flawlessly.
Choosing the Right Fiber Network Partner
Hiring a partner for your fiber network services is the single most critical decision you'll make during a deployment. A great partner is a force multiplier—they bring the kind of deep expertise that sidesteps expensive delays and guarantees a high-quality asset for years to come. On the flip side, the wrong choice can lead to blown budgets, missed deadlines, and a network plagued by chronic performance headaches.
This isn't about finding the lowest bidder. It's about finding a team with a proven track record of executing complex, multi-stage projects without a hitch. Think of it as your due diligence checklist for building a world-class network.
Vetting the Non-Negotiables
Before you even get into the weeds of project scope, there are some fundamental qualities every credible fiber provider must have. These are the deal-breakers, the things that separate the true professionals from the rest of the pack.
Your evaluation has to start with a serious look into these core areas:
- A Documented Safety Record: Ask to see their Experience Modification Rate (EMR) and proof of safety training. A genuine safety culture isn't just a talking point; it's what prevents accidents that bring projects to a grinding halt and create serious liability issues.
- Proven Mobilization Capabilities: How fast can they get skilled crews and specialized equipment to your job site? A partner with a solid logistics game can roll with the punches and keep your project on schedule.
- Meticulous Documentation Practices: Always ask for samples of their as-built documentation. Clean, accurate, and detailed records are absolutely essential for future maintenance, troubleshooting, and network upgrades.
A provider's approach to safety, logistics, and documentation offers a clear window into their overall operational excellence. These elements are leading indicators of how they will manage your project from start to finish.
Scrutinizing the Service Level Agreement
The Service Level Agreement (SLA) isn't just another piece of paper; it's a promise. This is where your potential partner puts their guarantees in writing, contractually committing to specific performance and quality standards. A vague SLA is a huge red flag. A strong one, however, gives you a clear framework for holding them accountable.
A solid SLA should clearly lay out:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): These need to be specific and measurable standards for things like splice loss, optical return loss, and other network performance benchmarks.
- Response Times: What are the guaranteed timelines for them to respond to network faults or maintenance calls after the project is complete?
- Remedies and Penalties: There must be clear consequences if the provider fails to meet the standards they agreed to uphold.
This document should be the foundation of your partnership, creating transparent and objective measures for success.
Assessing Their Ability to Scale
Finally, you need to be sure the provider can handle the sheer scale and complexity of your project—not just for today, but for your future needs as well. A crew that’s great at small, straightforward builds might not have the resources, processes, or experience to manage a massive, multi-year deployment.
Get right to the point and ask some direct questions to gauge their experience:
- Can they show you case studies from projects that mirror yours in scope and complexity?
- What is their process for managing projects with multiple phases and overlapping timelines?
- How do they handle the curveballs, like unexpected permitting delays or navigating difficult terrain?
Choosing the right partner is all about building confidence. By thoroughly vetting their safety, processes, SLAs, and real-world experience, you can move forward knowing you've selected a team that can deliver your network on time, on budget, and to the highest possible standard.
Navigating Common Challenges in Fiber Deployment
Even the best-laid plans for a fiber deployment can hit a snag. The real test of a project isn't avoiding problems altogether—it's how you navigate them. This is what separates a project that lands on time and on budget from one that gets bogged down in costly delays.
Think of it this way: every unexpected issue, whether it’s a permitting delay or a supply chain hiccup, chips away at your return on investment. A deployment that proactively manages these hurdles minimizes overruns, prevents future operational headaches, and ensures the network becomes the strategic asset it was designed to be.
Overcoming Permitting and Right-of-Way Delays
One of the most notorious bottlenecks in any fiber build is getting the right permits and securing right-of-way access. You're often dealing with a tangled web of municipal agencies, utility companies, and private landowners, and each has its own rulebook and timeline. A single hold-up can bring everything to a grinding halt for weeks.
To keep the ball rolling, seasoned partners know the drill:
- Early Engagement: The permitting process should kick off during the initial design phase, not as an afterthought.
- Strong Relationships: Having established connections with local authorities and utility owners can make a world of difference in smoothing out the approval process.
- Meticulous Paperwork: It’s all about getting the applications right the first time to avoid the back-and-forth of rejections and revisions.
Cutting through this red tape isn't just a box to check; it’s a cornerstone of any effective fiber network services strategy.
Managing Unforeseen Ground Conditions
What’s buried underground is often the biggest wild card. Crews can run into anything from solid rock formations and high water tables to a maze of unmarked utility lines. Striking a gas or water line is more than just a setback—it's a dangerous and expensive mistake.
A huge part of the job is making sure you don't hit existing underground utilities. This is where precise techniques like potholing in construction come into play. By safely exposing and verifying the exact location of buried infrastructure before major digging starts, crews can drastically reduce the risk of an accident. It's a fundamental step for any team that's serious about safety and sticking to a budget.
Mitigating risk is the cornerstone of protecting ROI. By addressing potential ground conflicts before they become active problems, you safeguard your project timeline and prevent the kind of budget-draining emergencies that can derail an entire deployment.
Mitigating Supply Chain and Stakeholder Issues
Today's projects face a double whammy: global supply chain snarls and local community concerns. A shortage of a specific fiber cable or connector can stop work in its tracks. At the same time, residents and business owners will naturally have questions about construction in their neighborhood.
Smart strategies for handling these variables include:
- Strategic Procurement: Ordering materials with long lead times well in advance and working with multiple suppliers is key. You never want to be dependent on a single source.
- Transparent Communication: It’s crucial to engage with the community early and often. Providing clear information about the project’s timeline, process, and benefits helps build support and head off potential opposition.
When you treat these challenges not as roadblocks but as manageable parts of the process, your deployment stays on track. A skilled partner ensures your network gets built efficiently, turning it from a simple expense into a resilient, long-term asset that will anchor your connectivity for years to come.
Your Questions About Fiber Network Services, Answered
When you're diving into the world of fiber optic networks, you're bound to have questions. We get it. Here, we’ve put together some straightforward answers to the questions we hear most often, drawing from our years of experience in the field.
How Long Does Fiber Optic Cable Actually Last?
You can expect a properly installed and well-maintained fiber optic cable to last for over 25 years. The glass fibers at the core are incredibly resilient and don't degrade like traditional copper wiring, making fiber an excellent long-term investment.
What really determines that lifespan is the quality of the protective outer jacket and the environment it's in. A cable tucked safely inside an underground conduit will naturally fare better and last longer than an aerial cable exposed to sun, ice, and wind.
How Much Can "Make-Ready" Work Affect My Project Timeline?
Make-ready engineering can be one of the biggest wildcards in any fiber deployment. It's the essential prep work needed to clear a path for the new fiber, whether that means making space on a utility pole or ensuring an underground conduit is usable.
It's no secret in the industry that getting permits and coordinating with pole owners—like the local power or phone company—is where schedules often get derailed. That's why any experienced partner will tell you to build a healthy buffer for the make-ready phase right into the initial project plan. Don't skip this.
What's the Real Difference Between Single-Mode and Multi-Mode Fiber?
The main distinction comes down to the size of the glass core that the light signal travels through. An easy way to think about it is comparing a narrow pipe to a wide one.
- Single-mode fiber uses a tiny core (about 9 microns) that forces light to travel in a single, straight path. This precision is perfect for long-haul, high-bandwidth connections, like the ones linking cities or connecting massive data centers, because the signal can travel for miles with minimal loss.
- Multi-mode fiber has a much larger core (50 or 62.5 microns), allowing light to bounce around in multiple paths. It’s a great, cost-effective choice for shorter distances—think wiring an office building or connecting buildings across a campus—but it just can't handle the demands of long-distance routes.
Why Do You Emphasize Network Documentation So Much?
Because accurate documentation is the lifeblood of a healthy network. These records, known as "as-builts," are the definitive map of what was actually installed in the ground or on the poles. They are absolutely critical for everything that comes next: maintenance, troubleshooting, and future upgrades.
Without a detailed blueprint, a simple repair can turn into a costly, time-sucking expedition to find the right cable. Good documentation protects your investment and ensures your network can be managed efficiently for decades to come.
At Southern Tier Resources, we bring the hands-on expertise needed for every step of a fiber deployment, from the first design sketch to the final as-built documents and ongoing maintenance. See how we build networks that last at https://southerntierresources.com.



